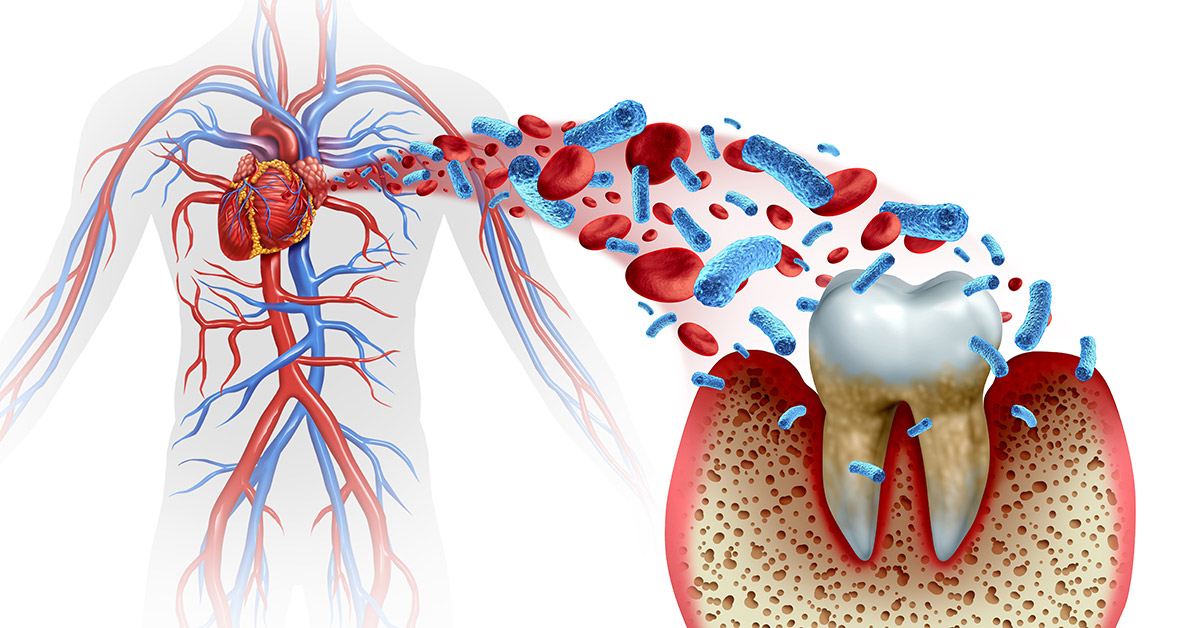
The Link Between Oral Health and Heart Disease: What You Need to Know
The Relationship between heart and oral health is very important to understand. When most of us think about maintaining good health, our focus is often on what we eat, how much we exercise, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking. However, an aspect of health that many overlook is the connection between oral health and overall wellbeing—especially heart health. Recent research has shown that the condition of your mouth can have a significant impact on your heart, potentially increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.

The Relationship Between Oral Health and Heart Disease
The mouth is home to millions of bacteria, some of which are harmless, while others can be harmful. These harmful bacteria thrive when oral hygiene is neglected, leading to gum disease (also known as periodontal disease). Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place and is caused by the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth.
Periodontal disease has been linked to a variety of serious health conditions, including heart disease. While the exact mechanism is still being studied, there are several ways researchers believe poor oral health may contribute to heart disease.
Inflammation: A Key Link between heart and oral health
One of the most critical connections between oral health and heart disease is inflammation. When gum disease occurs, the body responds with an inflammatory response. This inflammation can enter the bloodstream, leading to higher levels of inflammatory markers throughout the body. Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for the development of cardiovascular problems, including atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in the arteries), which can lead to heart attack or stroke.
Studies have shown that people with severe gum disease are more likely to develop heart disease, although the relationship is still under investigation. What is clear, however, is that reducing inflammation in the body—whether through treating gum disease or managing other lifestyle factors—can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular issues.
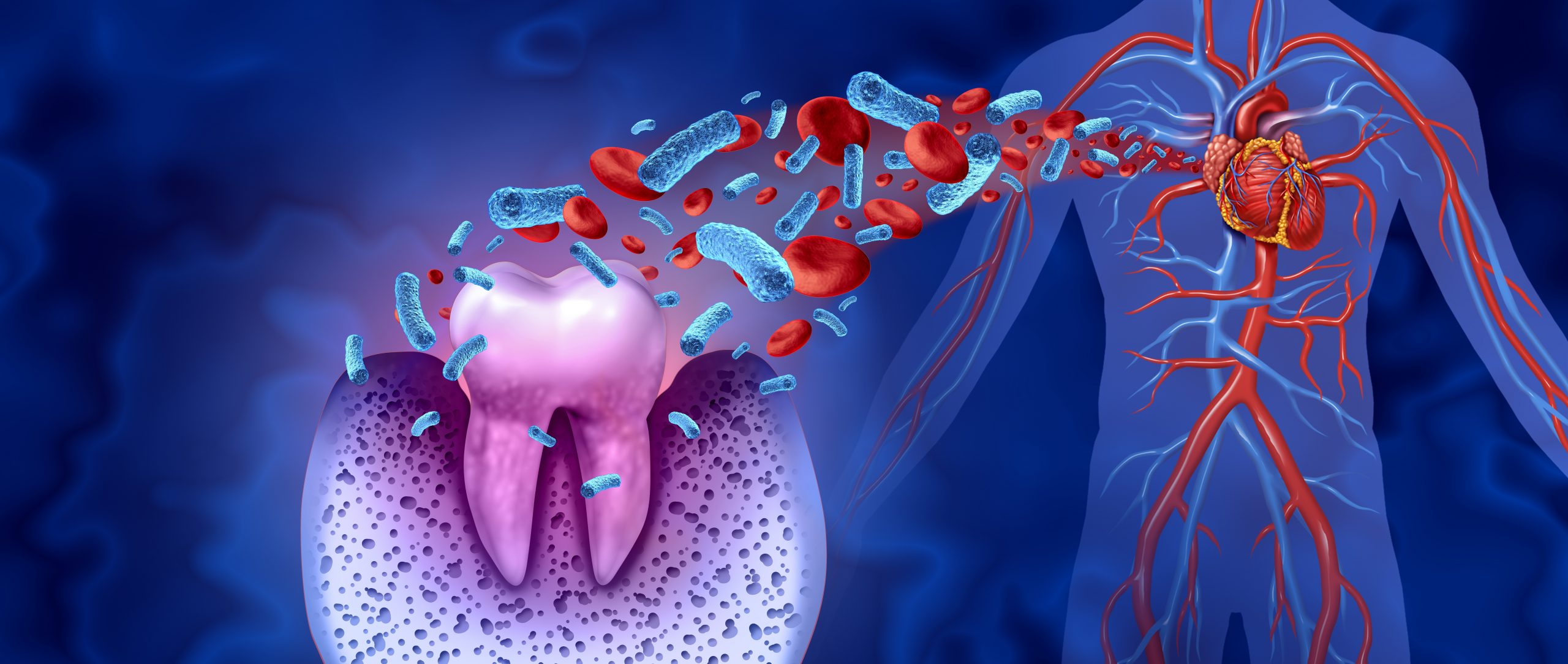
Bacteria from the Mouth Can Travel to the Heart creating a relation between two
Another way oral health impacts the heart is through the bacteria found in the mouth. When gum disease is present, harmful bacteria can enter the bloodstream through the gums and travel to other parts of the body. This can cause infections in various organs, including the heart. The bacteria may contribute to the formation of blood clots, which can block blood flow and increase the risk of heart attacks or strokes. So, relationship between heart and oral health should be considered.
The bacteria Porphyromonas gingivalis, commonly associated with gum disease, has been found in the plaque that builds up in arteries, further supporting the theory that oral bacteria can contribute to cardiovascular problems.
Risk Factors that Overlap
Certain lifestyle factors that increase the risk of heart disease also put your oral health at risk. Smoking, for example, is a major cause of both gum disease and heart disease. Smoking contributes to the buildup of plaque on teeth and also reduces blood flow to the gums, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. Similarly, poor diet, lack of exercise, and excessive alcohol consumption are risk factors for both oral and heart health issues.
It’s important to remember that while the link between oral health and heart disease is still being explored, the existing evidence is strong enough to suggest that maintaining good oral hygiene can benefit not just your teeth and gums, but also your cardiovascular health.
What You Can Do to Protect Your Heart and Mouth
Maintaining good oral hygiene is a simple yet effective way to reduce your risk of both gum disease and heart disease. Here are a few key practices to keep in mind:
- Brush and Floss Regularly: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing once a day can help remove plaque and prevent the buildup of harmful bacteria.
- Visit Your Dentist: Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for detecting early signs of gum disease and preventing further complications.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for both gum disease and heart disease. Quitting can improve your oral and cardiovascular health.
- Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can reduce inflammation in the body and promote both oral and heart health.
- Manage Stress and Blood Pressure: Chronic stress and high blood pressure contribute to both gum disease and heart disease. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and regular physical activity can benefit both your heart and mouth.
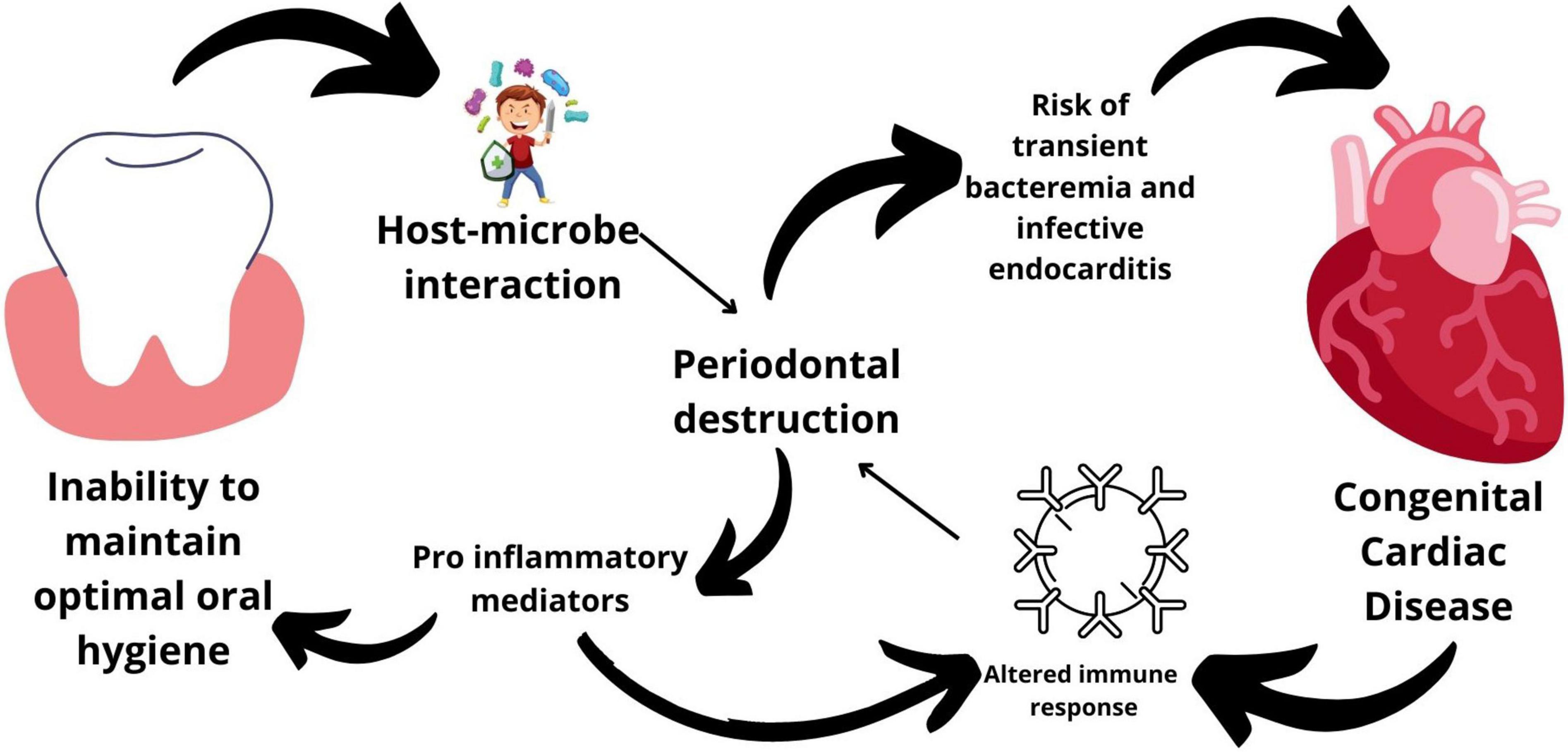
Conclusion
The link between oral health and heart disease is becoming increasingly clear, with research suggesting that good oral hygiene may be a simple yet powerful way to protect your heart. By brushing and flossing regularly, visiting your dentist, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can improve not only your smile but also your overall health. Taking care of your teeth and gums is an investment in your long-term health, so make it a priority to keep both your mouth and your heart in optimal condition. Relationship between heart and oral diseases should be top priority.